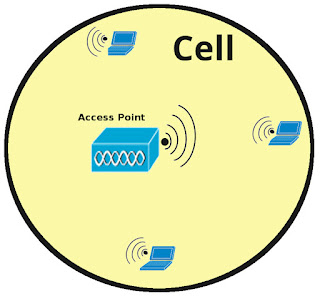
Every AP has a certain coverage area where its wireless signal is available. Any client which wants to connect to this access point should be available in this area. This coverage area is called a cell.
We have to choose the AP location according to the required coverage area.
If we want to increase the WLAN coverage area then we have to use more than one AP. The cells of one AP should overlap with other AP to avoid the disconnection of the clients.
When a client is in one cell it connects with the corresponding AP and as it moves it to another cell then it connects with another AP. Moving from one cell to another cell is called roaming.
When a client moves from one cell another, it disconnects from one AP and connects to the new AP.
Layer2 roaming will occur if the IP address of the client is unchanged. But if the IP address has changed means that the Layer 3 roaming had occurred.
If you want to reduce the number of APs to cover an area, then you should use the AP to the maximum transmit power. By doing this we are keeping the minimum cost.
If you use only one AP to cover an area by using maximum transmit power, then you have to face some drawbacks.
If one AP is used to cover a large area, then the number of clients accessing that AP will increase resulting in overcrowding.
As a result of this, the bandwidth allocated to each client will reduce.
We have to choose the AP location according to the required coverage area.
If we want to increase the WLAN coverage area then we have to use more than one AP. The cells of one AP should overlap with other AP to avoid the disconnection of the clients.
When a client is in one cell it connects with the corresponding AP and as it moves it to another cell then it connects with another AP. Moving from one cell to another cell is called roaming.
When a client moves from one cell another, it disconnects from one AP and connects to the new AP.
Layer2 roaming will occur if the IP address of the client is unchanged. But if the IP address has changed means that the Layer 3 roaming had occurred.
If you want to reduce the number of APs to cover an area, then you should use the AP to the maximum transmit power. By doing this we are keeping the minimum cost.
If you use only one AP to cover an area by using maximum transmit power, then you have to face some drawbacks.
If one AP is used to cover a large area, then the number of clients accessing that AP will increase resulting in overcrowding.
As a result of this, the bandwidth allocated to each client will reduce.