Down
This is the beginning state in forming the OSPF neighborship. In this state no hello's are received. So the neighborship is not formed in this state. The OSPF router begins sending hello's to the multicast address and moves to the INIT state.
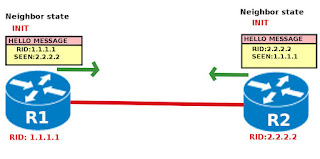
Init
In this state when the router receives a hello message from the other router, it checks the required conditions are matching or not. If the conditions to form the neighborships are matching then the router puts the RID of the other router in the hello message acknowledging that it received the other router's hello message and its ready to form the neighborship. When the other router receives the hello message which contains its own RID, the router moves to 2-way state. The same is the case with other router as well.
2-Way state
In this state the router looks for two types of LSA's.
1) The LSAs which are known to the neighbor but unknown to itself.
2)And the more latest version of the LSA's which it is aware of .
Exstart
The router has to learn the LSID's of all their known LSA's from each other. In order to learn the LSA's from the neighbor, the router will send the database description(DD & DBD) packet to the multicast address 224.0.0.5. Before sending the DD message the router moves to Exstart state. In this state, the master and slave election takes place. The router with higher RID becomes the master. After electing the master the transition to Exchange state takes place.
Exchange
In the Exchange state, both routers keep multicasting DD messages to each other. These DD message contain the LSA header. The header contains the LSIDs of the LSAs and their sequence numbers. The master router is responsible for the exchange of DD messages and the slave router simply responds to the master router. The exchange of DD messages between the master router and the slave router happens till both the routers have the same view of all the LSIDs in that area. After this point, the routers will move to the Loading state.
Loading
In this state the exchange of full LSAs between the two routers takes place. The router will send the Link State Request(LSR) message to the other router. The LSR will contain the LSID of the missing LSA.The other router will respond to the LSR with an Link State Update(LSU) which contains the LSAs requested. Once the router receives the requested LSA it will acknowledge it by sending a Link State Acknowledgement(LSAck) message or by sending the same LSA to the other router in an LSU message. Once all the LSA's have been exchanged the neighborship will move to FULL state.
Full
A router is in the FULL state means its LSDB is the same as the other router.